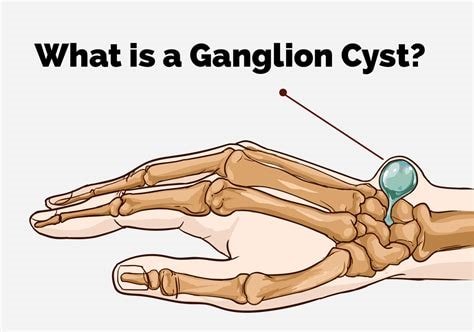
A ganglion cyst is a non-cancerous, round or oval sac filled with a jelly-like substance known as synovial fluid. Synovial fluid normally lubricates joints and tendons, helping reduce friction during movement. Ganglion cysts typically arise in the connective tissue around joints or tendons, most frequently near the wrist joint. They form when synovial fluid leaks out and accumulates in a sac outside the joint or tendon lining.
The most common locations for ganglion cysts include:
- Wrist (dorsal side): Near the tendons at the back of the wrist, a common site for ganglion cysts.
- Finger joints: Typically at the base of the fingers or around the knuckle joints.
- Ankle and foot: Although less common, cysts can form near the ankle joint or top of the foot.
Ganglion cysts are usually attached to a joint capsule or tendon sheath, which helps explain why they may vary in size and firmness, often fluctuating depending on activity or pressure.
Pathophysiology of Ganglion Cysts
The precise mechanism behind ganglion cyst formation isn’t fully understood, but it is believed to involve joint or tendon irritation and increased pressure within the joint capsule. When there is repetitive stress or strain on the joint or tendon, the lining may weaken, allowing synovial fluid to leak out and collect in a small sac, forming a cyst. Over time, the cyst can expand and become visible as a lump.
Several theories attempt to explain why ganglion cysts form, including:
- Trauma or Injury: Minor or repetitive injuries to the joint capsule or tendon sheath may weaken the area, resulting in synovial fluid leakage and cyst formation.
- Degeneration of Connective Tissue: Some cases may involve degeneration of the connective tissue, causing fluid buildup.
- Chronic Inflammation: Chronic irritation or inflammation in the joint capsule may also contribute to cyst development.
What Causes Ganglion Cysts?
Ganglion cysts are often linked to repetitive stress or mechanical strain on the affected joint, but other factors may contribute as well:
- Repetitive Motion and Overuse: Athletes or individuals who engage in repetitive hand or wrist movements, such as gymnasts or typists, are at higher risk.
- Injury: Prior trauma or injury to a joint or tendon may predispose someone to develop a ganglion cyst.
- Joint or Tendon Irritation: Conditions that put stress on tendons or joints, such as osteoarthritis, can increase the likelihood of ganglion cysts.
- Age and Gender: While ganglion cysts can affect anyone, they are more common in women and individuals between the ages of 15 and 40.
- Genetic Factors: Some people may have a genetic predisposition, as ganglion cysts occasionally run in families.
Homeopathic Remedies for Ganglion Cysts
These remedies focus on stimulating the body’s healing response, aiming to reduce the cyst’s size, relieve discomfort, and prevent recurrence.
- Ruta Graveolens: This remedy is frequently used for conditions involving joint and tendon pain, making it suitable for ganglion cysts. It’s especially helpful for individuals who experience pain in the wrist and hands from repetitive motion.
- Calcarea Fluorica: Known to support tissue health and strength, Calcarea Fluorica is useful for cysts that feel hard to the touch. This remedy may help dissolve cysts over time and reduce recurrence by strengthening the connective tissue.
- Benzoicum Acidum: Recommended for individuals with joint or tendon pain, Benzoicum Acidum is also effective in treating cysts and other growths on the joints, particularly in those with gout or arthritis.
- Silicea: Silicea is often used in cases where cysts are recurrent, as it promotes the expulsion of unwanted growths. It’s suitable for soft cysts or those that tend to refill and may help drain the cyst naturally.
- Graphites: This remedy is beneficial for cysts that appear with hard, lumpy textures. Graphites is recommended for those prone to skin issues and cystic formations.
- Causticum: Particularly helpful for ganglion cysts in individuals with stiff joints or a tendency toward rheumatism, Causticum may relieve discomfort in areas with limited mobility.
- Thuja Occidentalis: Known for addressing growths and cysts, Thuja is a versatile remedy used to treat ganglion cysts, especially if the cyst is soft and spongy. Thuja can help reduce cyst size and prevent recurrence.
- Hepar Sulphuris: For cysts that are sensitive to touch or prone to infection, Hepar Sulphuris may be helpful. It is especially effective for cysts that feel inflamed or cause localized pain.
- Lycopodium: This remedy is often prescribed for cysts in individuals with digestive issues or those prone to gas and bloating. Lycopodium can help in reducing cyst size and relieve related symptoms.
- Phosphorus: Suitable for cysts that are sensitive and tender, Phosphorus can support tissue healing. It’s also helpful for people who experience weakness or fatigue alongside their cyst symptoms.
Lifestyle Adjustments to Support Treatment of Ganglion Cysts
In addition to homeopathic remedies, certain lifestyle changes can support cyst management:
- Limit repetitive stress: Try to minimize repetitive movements, especially those that place strain on the wrists, hands, or ankles.
- Strengthening exercises: Physical therapy or gentle stretching exercises can help improve joint stability, supporting long-term joint health.
- Anti-inflammatory diet: Incorporate foods with anti-inflammatory properties, such as leafy greens, nuts, seeds, and fatty fish, to support tissue health.
If you are looking for ways to treat any joint issues with an individualized treatment plan approach then BOOK A FREE DISCOVERY CALL TODAY.
