Ear infections are common and often painful conditions that can affect individuals of all ages. They are especially prevalent in children but can also impact adults, causing discomfort, temporary hearing loss, and even fever in some cases. In this blog, we’ll explore the anatomy and physiology of the ear, examine the causes of ear infections in both children and adults, discuss preventive strategies, and homeopathic remedies for managing ear infections.
Anatomy and Physiology of the Ear
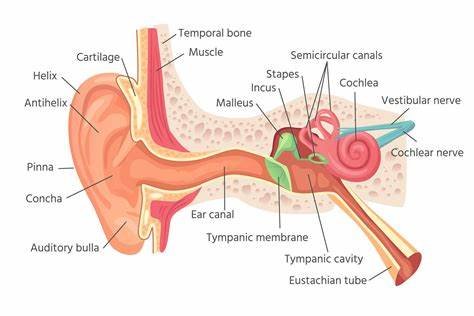
The ear is a complex organ involved in both hearing and balance. It is divided into three main parts: the outer ear, middle ear, and inner ear, each playing a unique role in auditory processing and balance.
- Outer Ear: This includes the pinna (or auricle) and the ear canal. The outer ear captures sound waves and channels them into the ear canal towards the eardrum.
- Middle Ear: The middle ear contains the eardrum (tympanic membrane) and three small bones known as ossicles—the malleus, incus, and stapes. These bones amplify sound waves and transmit them to the inner ear. The Eustachian tube, which connects the middle ear to the back of the throat, helps maintain pressure balance in the ear.
- Inner Ear: The inner ear houses the cochlea, which converts sound waves into nerve signals that the brain interprets as sound. It also contains the vestibular system, which assists with balance.
Ear infections commonly occur in the middle ear, especially when fluid builds up behind the eardrum, creating an environment where bacteria or viruses can thrive.
What Causes Ear Infections in Children?
Ear infections are particularly common in children because of the unique structure of their Eustachian tubes, which are shorter and more horizontal than in adults. This makes it easier for bacteria and viruses to travel to the middle ear. Some common causes include:
- Upper Respiratory Infections: Colds or viral infections can lead to fluid buildup in the middle ear, creating conditions for an infection.
- Bacteria and Viruses: Bacterial infections, especially those caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae or Haemophilus influenzae, are common culprits. Viral infections, like those caused by the flu or respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), also lead to ear infections.
- Allergies: Allergic reactions can cause inflammation in the nasal passages and Eustachian tubes, increasing the risk of fluid buildup and infection.
- Secondhand Smoke Exposure: Exposure to smoke can irritate the Eustachian tubes and make children more susceptible to infections.
- Bottle-Feeding: Babies who are bottle-fed while lying down may be at higher risk of ear infections due to the fluid’s potential to flow into the Eustachian tube.
What Causes Ear Infections in Adults?
While ear infections are less common in adults, they can still occur due to various factors:
- Sinus Infections and Colds: Respiratory infections can spread to the ear, especially if the Eustachian tube becomes blocked, trapping fluid and allowing bacteria or viruses to grow.
- Allergies: Inflammation from allergic reactions can block the Eustachian tube, making it more difficult for the ear to drain properly.
- Eustachian Tube Dysfunction: Age-related changes, injuries, or swelling due to infections can hinder Eustachian tube function, leading to fluid buildup and infections.
- Swimming or Water Exposure: Prolonged exposure to water, especially if it remains trapped in the ear canal, can lead to infections, commonly referred to as “swimmer’s ear.”
- Nasal Congestion: Adults with chronic sinusitis or other nasal problems may have Eustachian tube blockage, which can lead to recurring ear infections.
How to Prevent Ear Infections
There are several strategies to help reduce the risk of ear infections in both children and adults:
- Practice Good Hygiene: Regular handwashing helps prevent the spread of bacteria and viruses that can lead to respiratory infections.
- Avoid Secondhand Smoke: Exposure to smoke increases the risk of respiratory and ear infections, particularly in children.
- Breastfeed if Possible: Breastfeeding has been shown to reduce the risk of ear infections in infants.
- Limit Pacifier Use: Frequent pacifier use has been linked to an increased risk of ear infections in young children.
- Dry Ears after Swimming: For adults and children prone to outer ear infections (swimmer’s ear), drying the ears thoroughly after swimming can prevent infections.
- Manage Allergies: Proper management of allergies can reduce nasal congestion and inflammation that contribute to Eustachian tube blockage.
Homeopathic Remedies for Ear Infections
Homeopathy offers several remedies aimed at alleviating the symptoms of ear infections. Here are some commonly used remedies:
- Belladonna: Useful for acute ear infections with throbbing pain and redness. This remedy may suit people experiencing high sensitivity to touch and light, with sudden-onset symptoms.
- Pulsatilla: Often used when the pain is accompanied by thick yellow or green discharge and worsens in warm environments. This remedy is well-suited for children who are clingy and comforted by fresh air.
- Chamomilla: A popular choice for ear pain in children, especially if the child is irritable or inconsolable due to intense pain. This remedy may also help if the pain worsens at night.
- Hepar Sulphuris: Effective for ear infections with sharp, stabbing pain and sensitivity to cold air. It can be useful if there is a yellowish discharge from the ear.
- Mercurius Solubilis: Used for infections with discharge, particularly when the ear has a foul smell, and symptoms worsen at night or in damp conditions.
Additional Homeopathic Remedies for Ear Infections
In addition to the main remedies, there are other homeopathic remedies that may be beneficial for specific types of ear infections:
- Calcarea Carbonica: Ideal for recurring ear infections, especially in individuals with a tendency toward congestion and swollen glands. It is often used for children with chronic infections.
- Silicea: Recommended for chronic or persistent ear infections with thick discharge, especially if symptoms worsen in cold conditions or at night.
- Aconitum Napellus: Used for the early stages of ear infections, particularly if symptoms appear suddenly after exposure to cold or wind. Aconite may help if the ear pain is accompanied by a fever.
- Lachesis: Beneficial for ear infections with sharp, pulsating pain, particularly if symptoms are worse on the left side and feel better with warmth.
- Graphites: Used for cases with chronic ear discharge, particularly if it is thick and sticky. Graphites may be suitable for individuals with eczema or other skin conditions.
Conclusion
Ear infections can be painful and disruptive, but understanding their causes and treatment options can help manage symptoms and promote healing. Maintaining good hygiene, managing allergies, and avoiding irritants can prevent infections, especially in children. Chronic or severe cases should always be evaluated by an experienced Homeopath to ensure proper care and avoid complications.
If you are suffering from chronic or recurrent ear infections or conditions BOOK A FREE DISCOVERY CALL TODAY to start your journey towards healing in the natural way.
